Advanced Fields
These fields are designed for more complex scenarios and may require additional configuration or technical knowledge. They are ideal when you need to connect data, run custom actions, or create fully customized user interfaces.
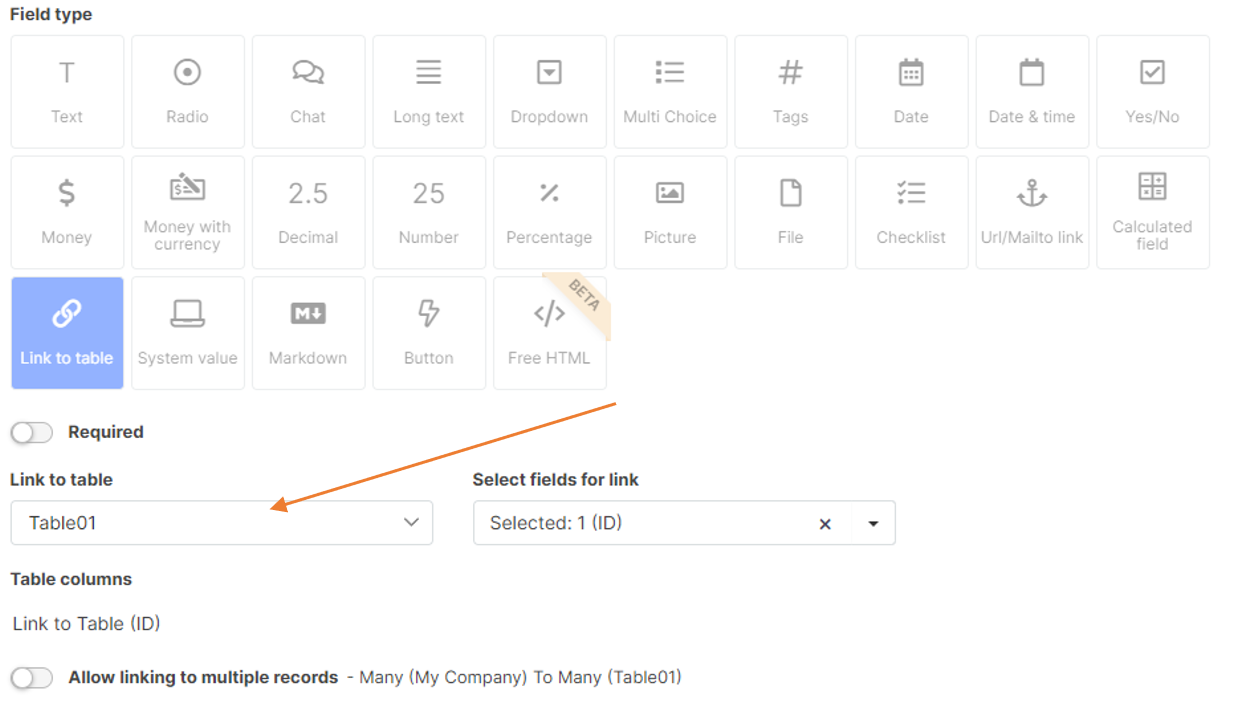
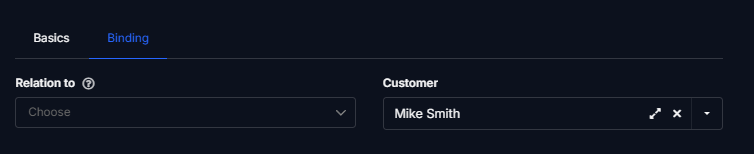
Link to Table
It is a field you can use to link to another table in your Tabidoo.
In Table Item Settings, you specify the tables with which you want to work. See more in the chapter - Type of Binding.
Link to Table field for linking other tables
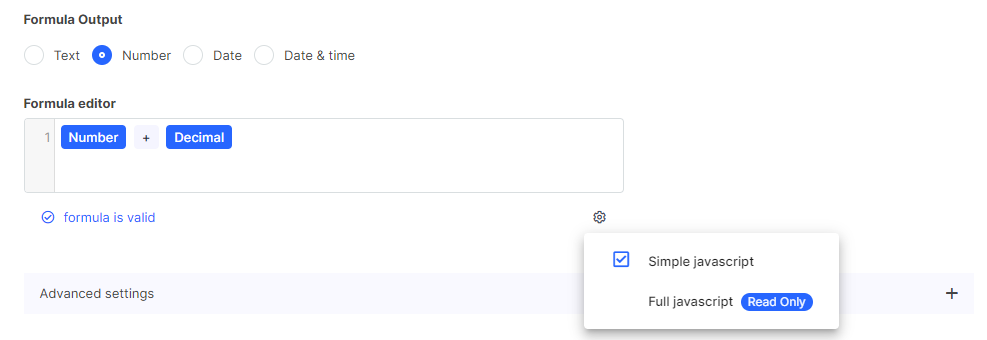
Calculated Field
It is a field that allows you to perform basic arithmetic operations with other fields. For instance, it can add a quantity field to a price field. Or it can assign a First Name field to another Last Name field.
In Table Item Settings, you specify the fields which you want to work with.
Calculated Field for arithmetic field operations
Note:
Calculated Fields in Tabidoo are dynamic—they are recalculated whenever the record is updated or when relevant dependent fields change. The calculation result is not stored permanently; it is generated based on the current data. For linked table fields, recalculation occurs only when the current record itself is modified. For scenarios requiring updates triggered by changes in linked records, or for more complex logic, consider using automation workflows or scripting.
For more details, examples of supported functions, and advanced usage tips, see the Calculated Fields article.
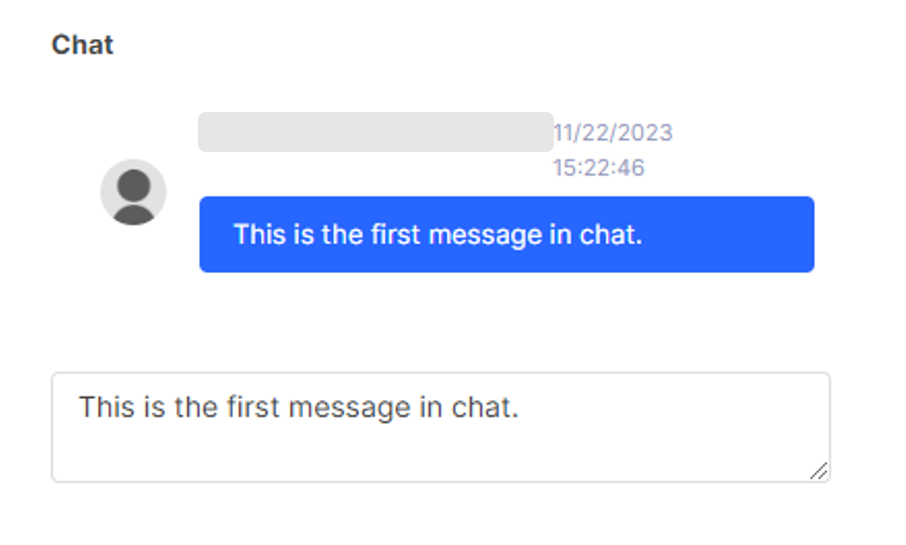
Chat
It is a discussion between the users of the given database. It is suitable for commenting on the content or for important remarks. You can use it for notes or revisions.
Chat field for comments and discussions
The chat can also work in real-time mode. In this case, messages are sent when the Enter key is pressed, and all messages are immediately saved to the log. If other people are viewing the record at the same time, they can see and reply to the messages instantly. You can also notify specific users you want to chat with.
You can mention a user to draw their attention by typing the @ symbol followed by their username (or selecting it from the user list). Mentioned users will receive a notification—either in Tabidoo (if they have the site open) or via email if applicable. If someone is part of the chat or is directly mentioned, they will receive a notification according to their notification settings.
Note:
Real-time behavior is not available for new records—chat becomes active only after the record is saved.
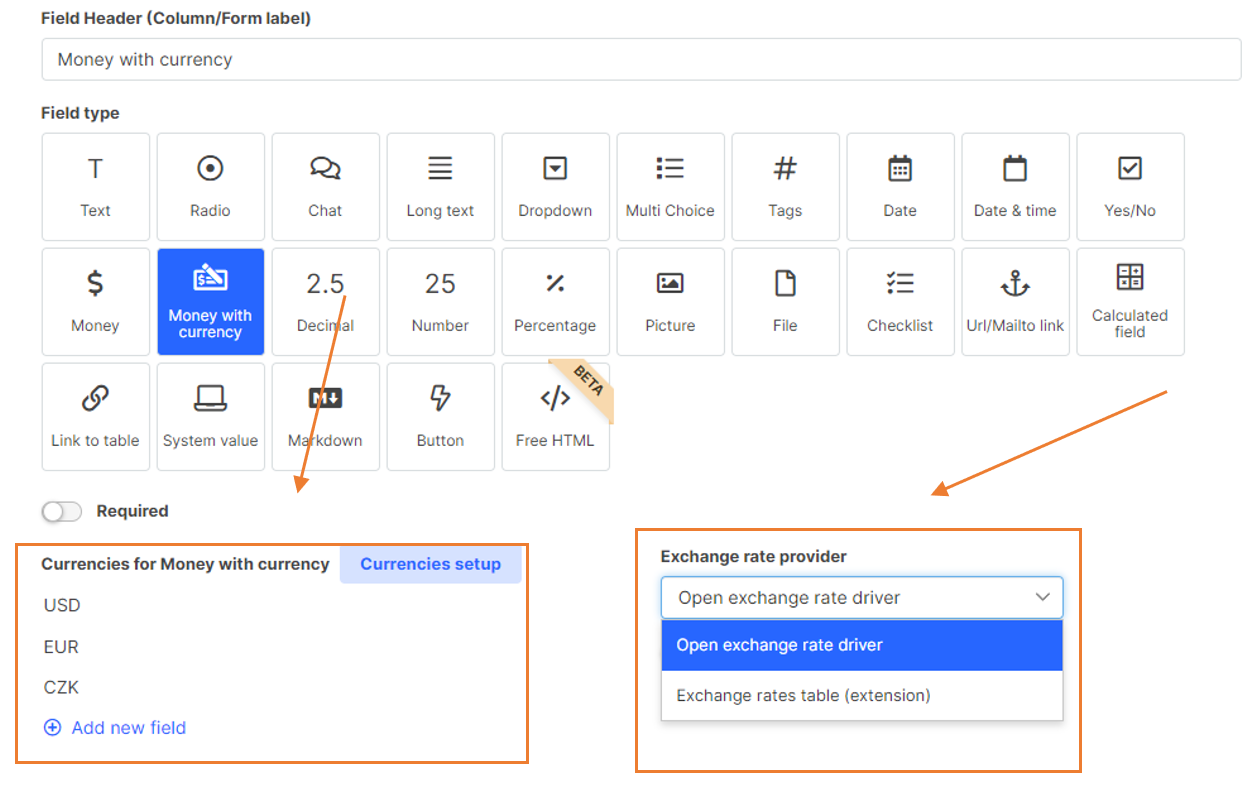
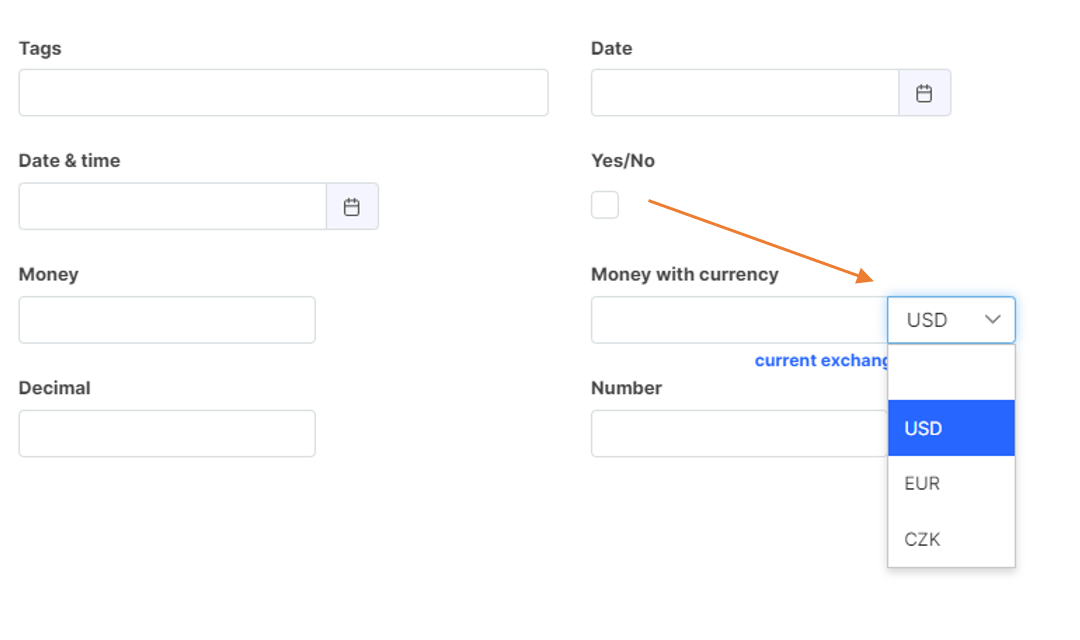
Money With Currency
This field is used to enter and automatically convert money between currencies.
Field type Money With Currency for the automatic money conversion
Firstly, you have to add the currencies you want to work with by clicking on the "Add new field" button under the "Currencies for Money with currency" section. Secondly, you can choose to automatically load the exchange rate according to the internet provider or you can define your own rates in the Exchange Rates extension.
Exchange Rates extension can be extended with any additional columns. For example, the exchange rate type. For the input field, you can then restrict what type of rate is used for conversion.
Field type Money With Currency for the automatic money conversion
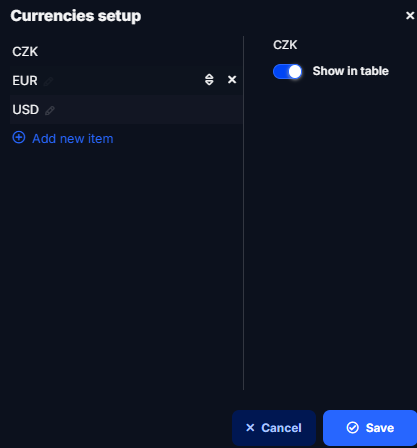
Currency Display Setup in the Table
In the Currencies setup section, you can define which currencies will be shown directly in the table (grid).
Steps:
- Click on the Currencies setup button.
- On the left side, you will see all added currencies (e.g., CZK, EUR, USD).
- Select a currency to open its settings on the right panel.
- Use the Show in table switch to control the visibility
- Confirm your changes by clicking Save.
Markdown
The Markdown field is a text editor designed for writing and formatting content using the Markdown syntax—a lightweight markup language that allows you to format text with minimal use of tags. It is commonly used for documentation, notes, and content intended for websites or version control repositories such as GitHub.
In Tabidoo, the Markdown field lets you enter and format text directly in Markdown while providing basic editing tools and a preview of the rendered output. This makes it easy to create structured, readable content such as bullet lists, headings, links, and tables without using complex HTML.
For more details about the Markdown syntax, see the Markdown language wiki.
Button
The Button field type enables you to run any script directly from your form in Tabidoo. All you need to do is insert your script into the scripting editor in the table field settings.
The script will be run when the button on the form is pressed.
Example:
The following script opens a form from the Tasks table with a pre-filled Customer field (field type Link to Table) using the current record’s ID:
doo.form.saveAndStay();
// Optional: example of passing additional form options
/* let options = <IOpenFormOptions>{};
options.model = {
}; */
doo.form.openForm('tasks', {
model: {
customer: { id: doo.model.id }
}
});
This approach allows you to quickly create related records with certain fields already filled in, streamlining the data entry process.
FreeHtml Input (Beta)
The FreeHtml Input field type allows you to extend Tabidoo with your own custom input type. It is currently in Beta – functionality and behavior may change.
FreeHtml Input is based on HTML and JavaScript. Please use only syntax supported by all major browsers. At the moment, scripts can interact with doo.model, but only the value and originalValue properties are supported.
The definition consists of
- HTML template – the markup for your custom element.
- Init script – runs when the field is loaded and can initialize event listeners or set default values.
- On-change script – runs whenever the form data changes, allowing you to synchronize the element with the model.
The placeholder string TBD-RANDOM-ID will be replaced by a random ID at runtime. Use it in your class or ID names to ensure the identifiers are truly unique.
Using external JavaScript
You can also use external JavaScript libraries with a FreeHtml Input. For details, see the article on using external JavaScript in Tabidoo.
Example of simple custom input binding:
In this example, we create a heading and an input box. The init script listens for changes in the input and updates the model. The on-change script takes the value from another field (code) and updates the heading text.
HTML template
<h5 class="{{TBD-RANDOM-ID}}-my-h1">Title</h5>
<input class="form-control {{TBD-RANDOM-ID}}-my-input1" />Init script subscribes the change event of the text input and write the value into the form model after lost focus
function setupEvents() {
let titleInput = document.getElementsByClassName('TBD-RANDOM-ID-my-input1')[0] as HTMLInputElement;
titleInput.addEventListener('change', (event) => {
doo.model.text.value = titleInput?.value;
});
}
setupEvents();And the On Change script puts the value from the field "code" into DOM (title) element
function synchronizeData() {
let title = 'Values - ' + doo.model.code.value + '/' + doo.model.code.originalValue;
let titleElement = document.getElementsByClassName('TBD-RANDOM-ID-my-h1')[0];
titleElement.innerHTML = title;
}
synchronizeData();So we covered both ways in our case (from model to our input and back)
In case the value of the input field contains a property header, this is shown in the table cell. Otherwise the whole JSON.
doo.model.freeHtml.value = {
header: 'Label for grid',
data: ...
};